Tilapia Fishing: Essential Bait, Lures & Tackle
Tilapia Fishing: Essential Bait, Lures & Tackle
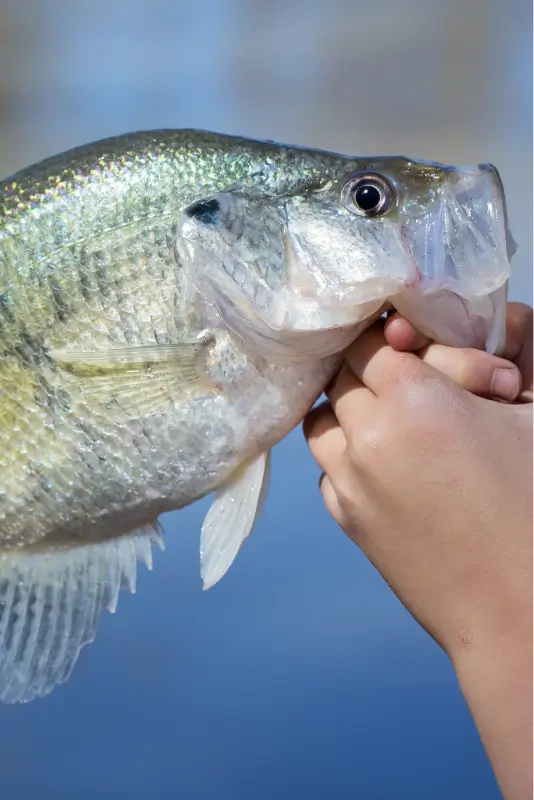
Fishing for tilapia is a fun and rewarding experience, especially for beginners or families looking to spend a relaxing day outdoors. These fish are popular for their mild, delicious flavor, but they’re also a blast to catch! Tilapia thrive in warm, freshwater lakes, rivers, and ponds, and they’re known for being active feeders, making them relatively easy to reel in.
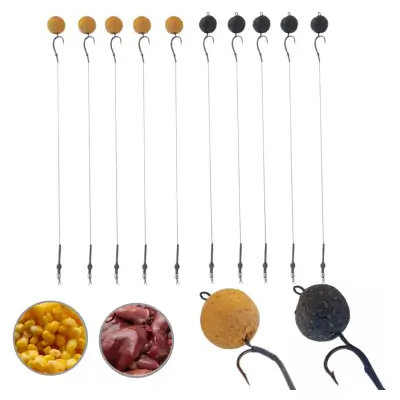
Tilapia are herbivorous, so their diet is a bit different from other game fish. They mainly eat algae, plants, and small aquatic critters. This means you’ll have the best luck using baits like bread balls, corn, or even small pieces of vegetables. Try casting your line near structures like rocks, vegetation, or shallow sandy areas where they often hang out.
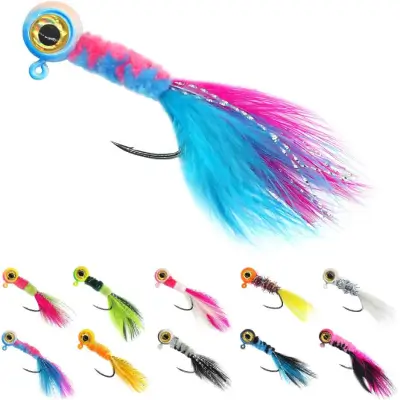
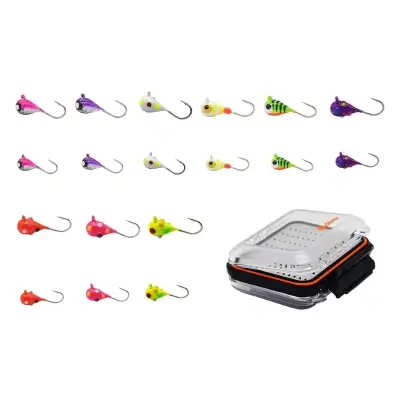
Light tackle works great for tilapia because they don’t put up a massive fight. Use a small hook and a simple bobber rig for the best results. Keep in mind that tilapia tend to nibble lightly, so pay close attention to your line.
Whether you’re fishing for fun or hoping to bring home dinner, tilapia fishing offers a relaxing and enjoyable time for anglers of all skill levels. Plus, they taste amazing fried, baked, or grilled! Give it a try and enjoy the day!
Tilapia Fishing Guide Fishing Facts
Location
Habitats
Diet
Activity